The consumption of natural rubber is linked to the development of the automotive industry and especially tires. This consumption is driven by growth in the emerging markets which include China and India.
Despite the slowing down of China and developing countries growth these past years, the total demand has however increased by an average of 4,6% per year from 2016 to 2018. It is however stable in 2019.
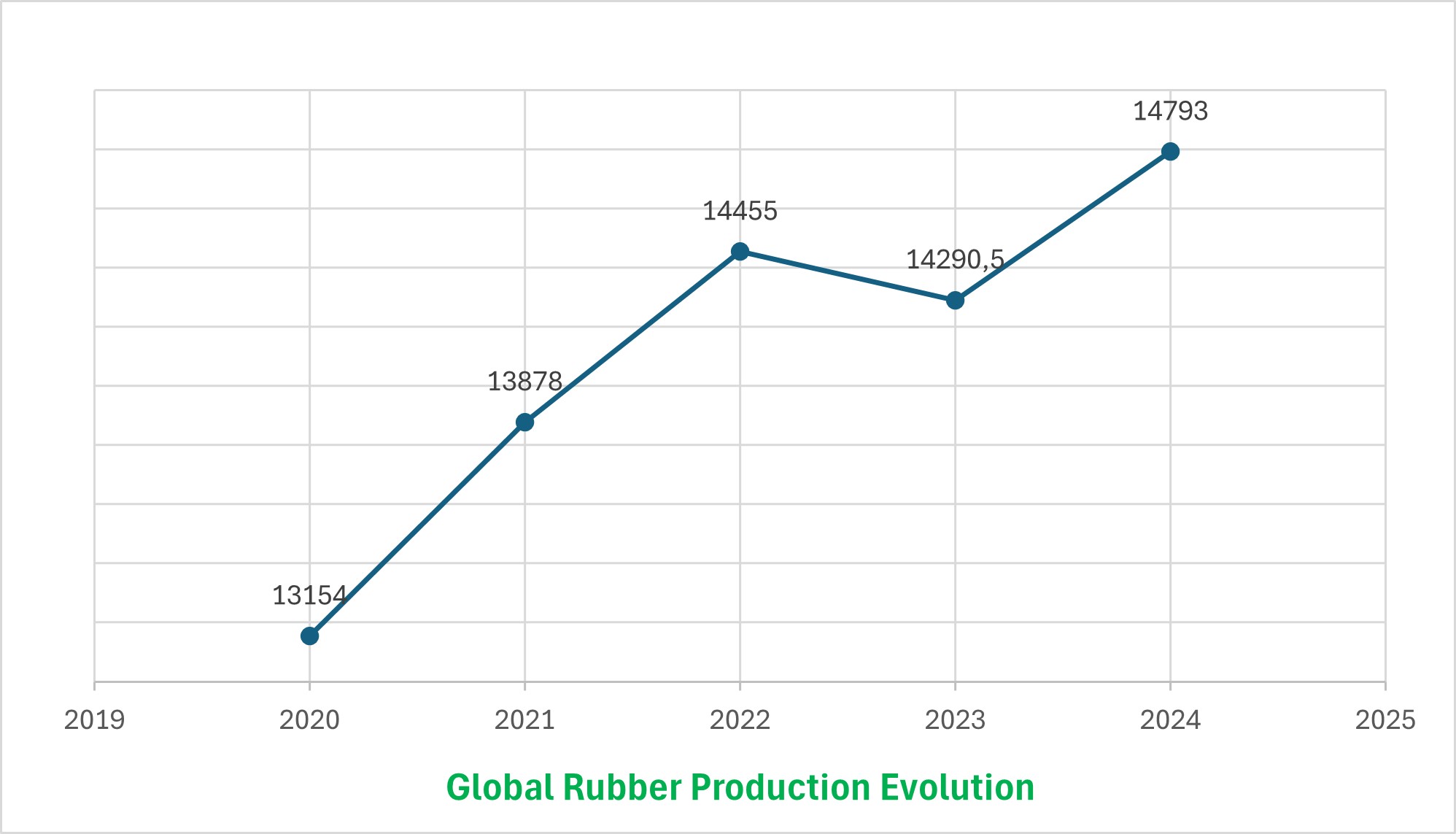
The offer had regularly risen until 2016 due to important plantings favored by top of cycle phase from 2005 to 2012. These plantings are now stabilized, but the rubber immaturity period of 7 years creates an inertia in the adaptation of supply to demand. However, production is stationary since 2017 and supply and demand are now balanced.
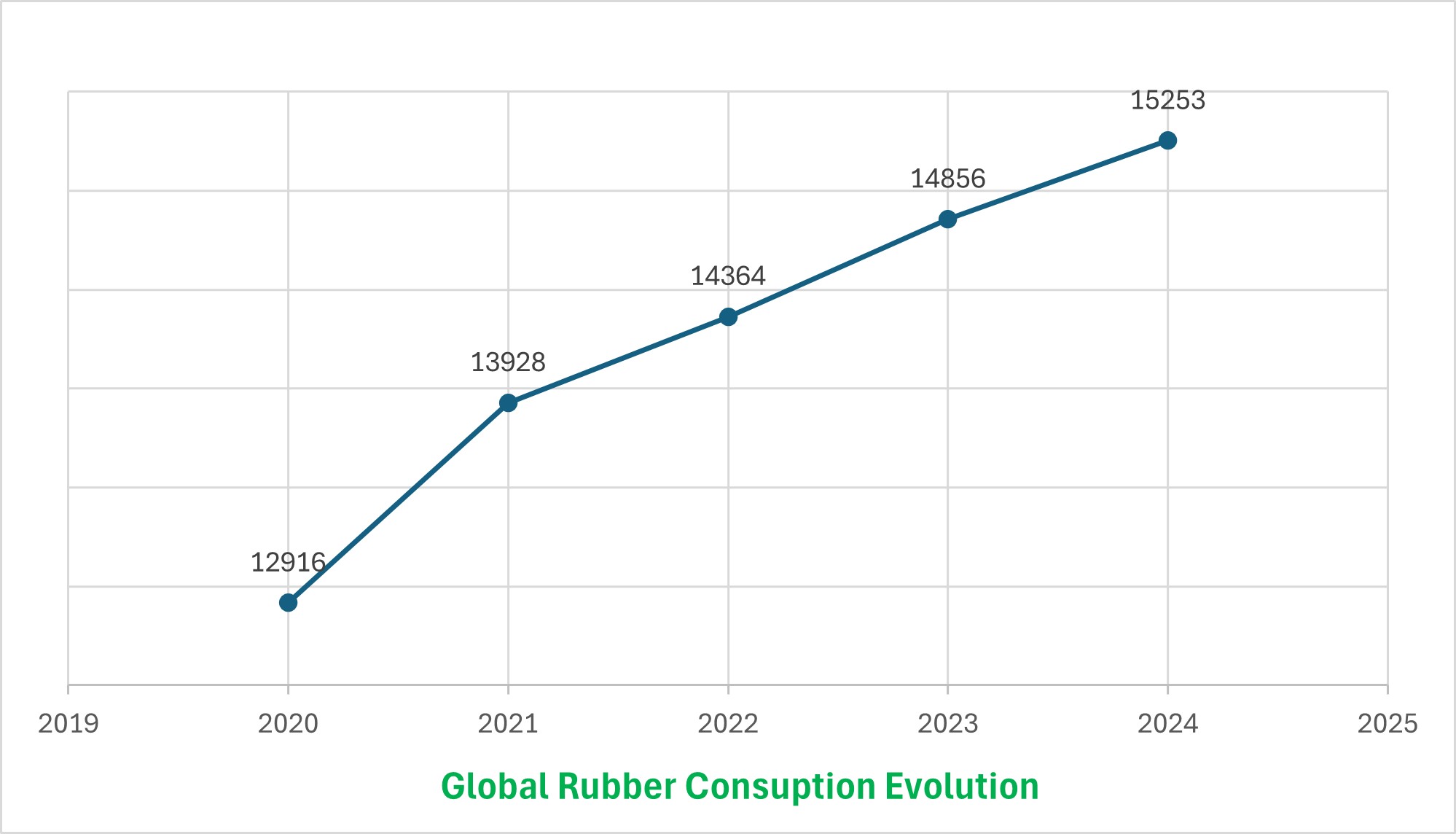
China's share of global rubber consumption has been around 30% since 2015, growing in line with global production.
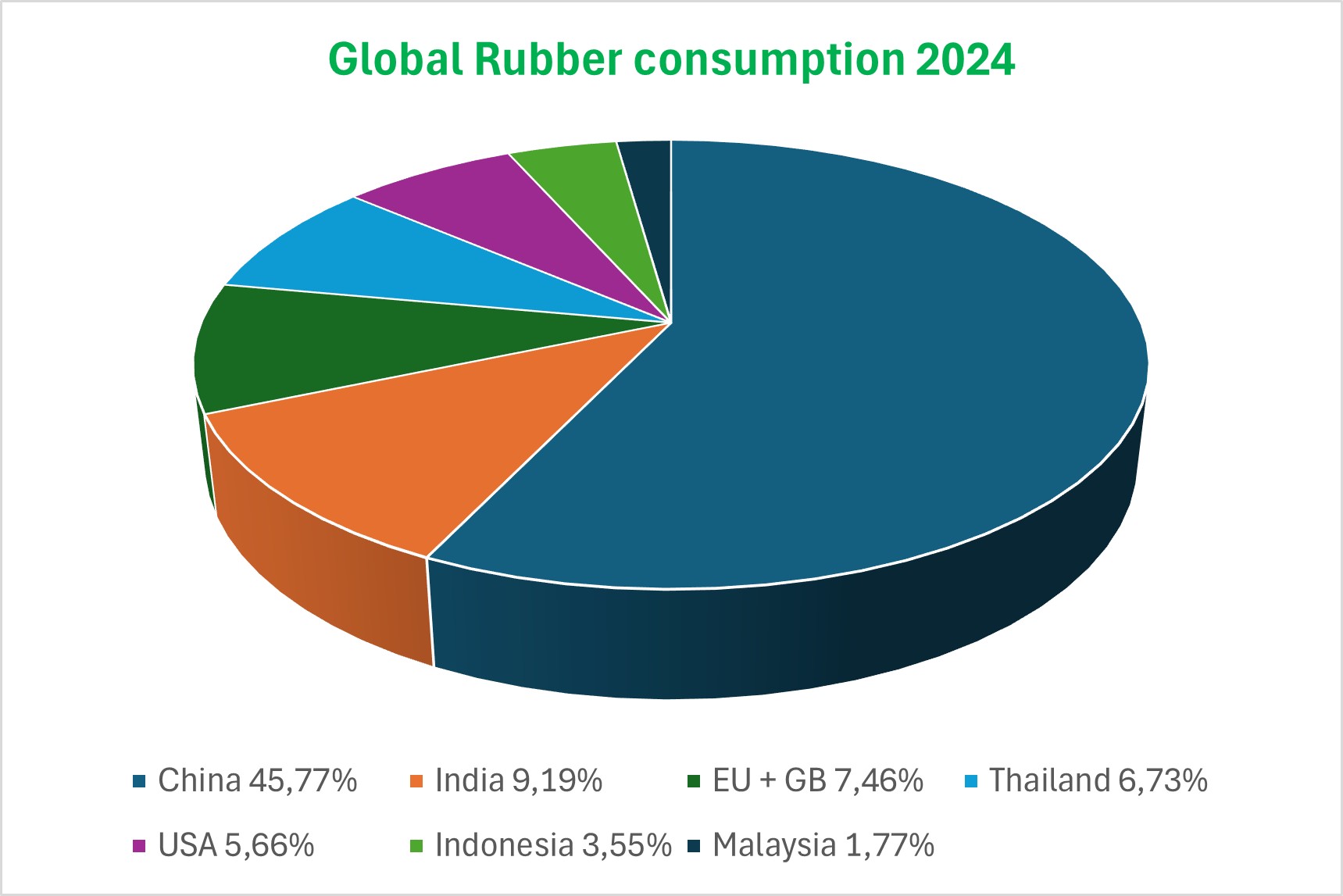
The global production of natural rubber totaled 13,6 million tons in 2019. Asia represents 90% of the this production.
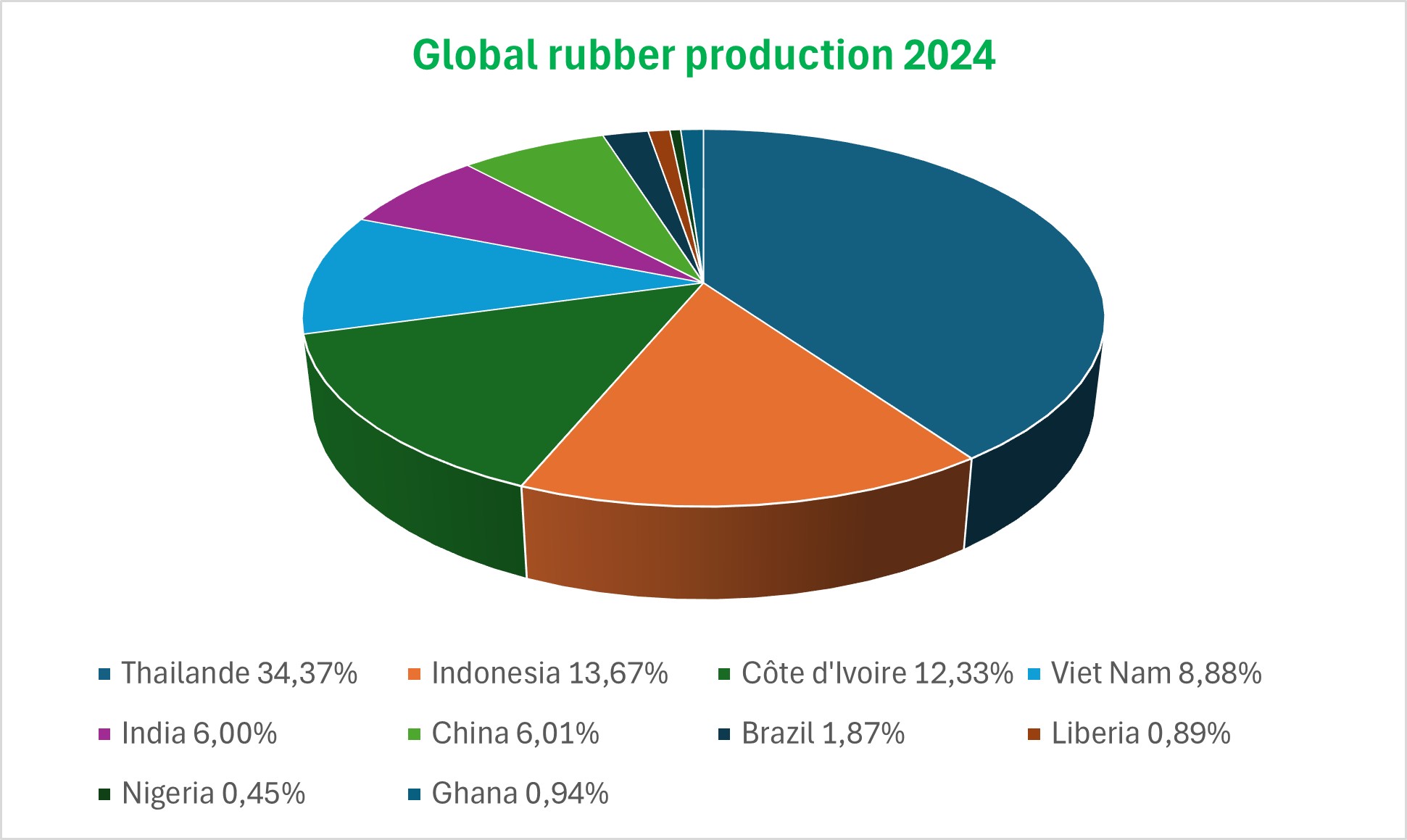
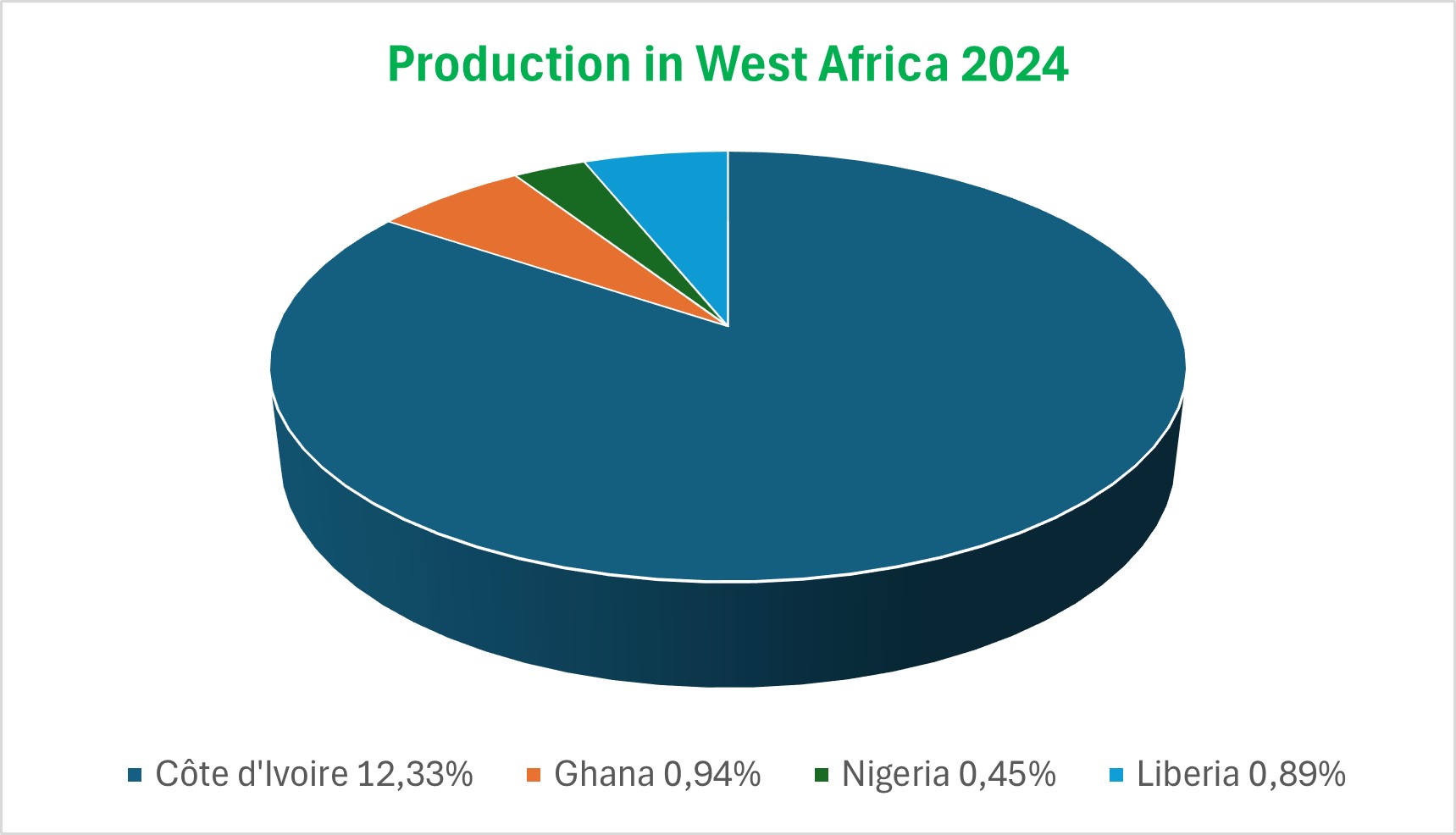
With a growing share of 8% of the world’s production, West Africa offers an ideal development potential for the production of rubber with its favourable climatic conditions, large areas of available non forest land and farm workers.
African rubber, which stands at 1.1 million tons, is finding a natural outlet in the European market.
Natural rubber demonstrates characteristics that gives it a competitive advantage to synthetic rubber: a lower heat generation and a better ability to regain its original shape. Such qualities are essential for tires, an especially for heavy goods vehicles, agricultural vehicles, aircraft and civil engineering. The substitution between natural rubber and synthetic rubber therefore remains limited for such applications.
The share of natural rubber compared to synthetic rubber moved from less than 40% in the 2000s to more than 47% today.
Many industries have ambitious goals to reduce their carbon footprint and raise the renewable material quantities in their products, so the evolution of the proportion natural rubber/synthetic rubber is an opportunity.